
Emerald Ash borer
LATIN NAME: Agrilus planipennis
RANGE: Native to Asia, likely arrived via cargo ship. Currently spreading west and south as per the below map (eff 2/2017)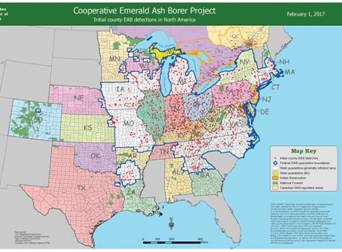
DESCRIPTION: Adults are a bright, metallic green with darker green “cover wings” and a bright red upper abdomen. 

 SYMPTOMS: Weak and thinning ash crowns, branches with yellowing leaves, epicormic shoots or suckers on ash limbs and trunks, bark splits, and D-shaped exit holes on the trunk.
SYMPTOMS: Weak and thinning ash crowns, branches with yellowing leaves, epicormic shoots or suckers on ash limbs and trunks, bark splits, and D-shaped exit holes on the trunk.
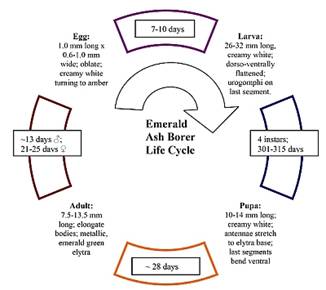
LIFE CYCLE: Cycle can cover one to two years. After emergence, adults feed for one week (little damage is caused) and then mate. Eggs are deposited between bark crevices, flakes, or cracks and hatch about two weeks later. After hatching, larvae chew through the bark to the inner phloem, cambium, and outer xylem where they feed and develop. EAB has 4 larval instars. In fall they develop into pupae, and adults that emerge through holes chewed in the bark the following spring.
HOST PLANTS: Ash trees
FEEDING HABITS: Adult beetles lay eggs on the bark of ash trees. When the eggs hatch, the larvae bore into the bark and feed on the transportation tissues of the tree. This disrupts the movement of nutrients and water within the tree, girdling it and causing tree death.
